| Sensitivity Issues in Step-Scan FT-IR Spectrometry 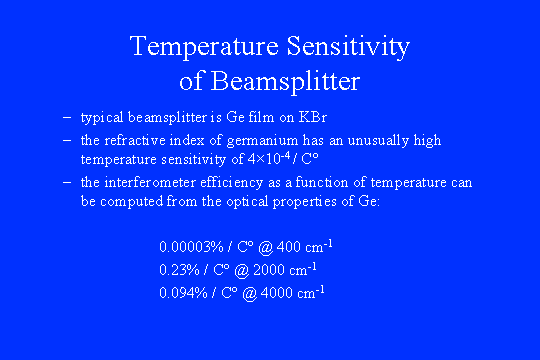
The beamsplitter's sensitivity to temperature
fluctuations arises from the germanium layer. Germanium is a semiconductor with a low
bandgap energy. The optical properties are dominated by free and loosely bound charge
carriers; the population of charge carriers and the bandgap energy both vary rapidly at
room temperature. The bottom line is that the interferometric efficiency will change by
0.25%/°C in the middle of the spectral range. The changes are probably slow (and
therefore not a serious noise source) because the germanium is sandwiched between two
slabs of KBr (which is a poor conductor of heat). However, this is a likely source of
unstable baselines in some commercial rapid-scan FT-IR spectrometers.
|