| Sensitivity Issues in Step-Scan FT-IR Spectrometry 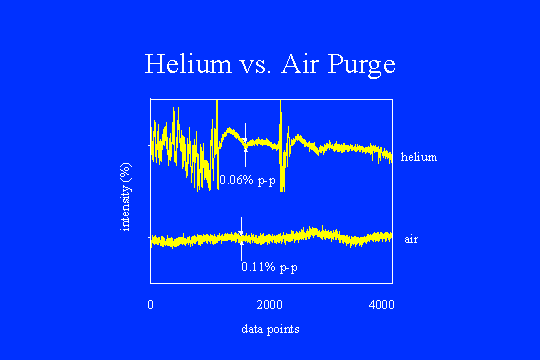
Another approach to improving the stability would be
to use a purge gas having a smaller refractive index, and consequently, a smaller change
in refractive index with temperature. Helium has approximately 10x smaller non-vacuum
contribution to the refractive index than air, and a correspondingly smaller dn/dt. This
slide does not show what was intended, namely a 10x improvement in stability. However, it
does show that purging the spectrometer is itself a serious noise source. The left side of
the trace was recorded while the helium flow was 40 cubic feet per hour (the recommended
purge rate). As soon as the flow was turned off, the noise was greatly reduced to about
0.06% p-p (compare to 0.11% for "still" air). A useful experiment would have
been to purge with air or nitrogen to compare to the disturbance created by helium. It
should be 10x worse.
|