| Sensitivity Issues in Step-Scan FT-IR Spectrometry
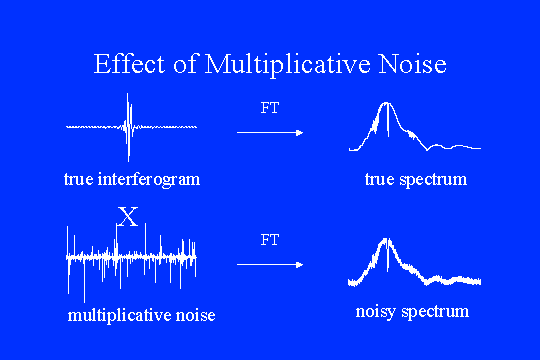
A noise-free interferogram transforms to a noise-free spectrum. If multiplicative noise affects the interferogram, the Fourier transform of the noise function is convolved with the true spectrum. In step-scan measurements, the instrument can drift significantly between sampling points (steps). In rapid-scan measurements, the same drifts occur but the instrument condition remains approximately the same for the period of a single mirror sweep. Thus, the drift multiplies the entire interferogram by a constant value, influencing the apparent spectral energy, but not introducing high-frequency noise into the spectrum. |